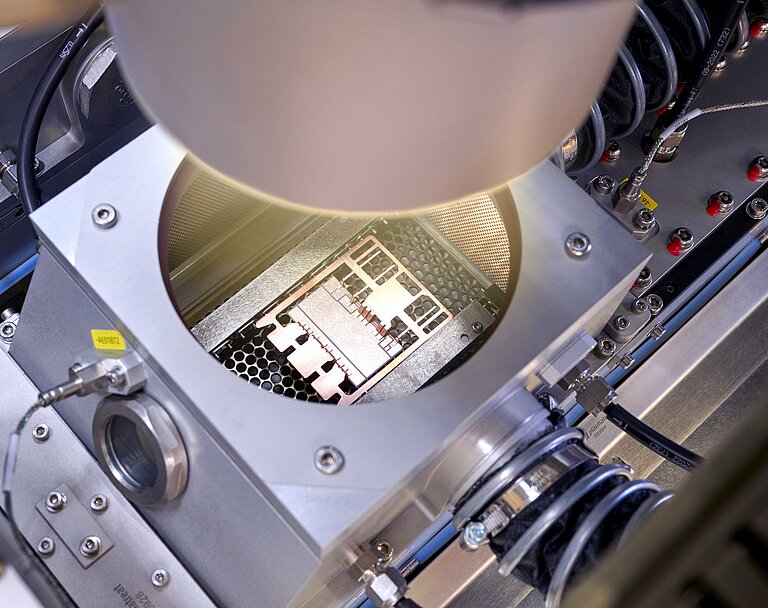
Plasma Technology in Action – Live at PCIM Europe 2025
Power modules are the core of modern power electronics – whether in e-mobility, industrial automation, or renewable energy applications. From May 6–8, 2025, Plasmatreat will be showcasing how plasma technology can significantly enhance the performance and reliability of these critical components at PCIM Europe in Nuremberg.
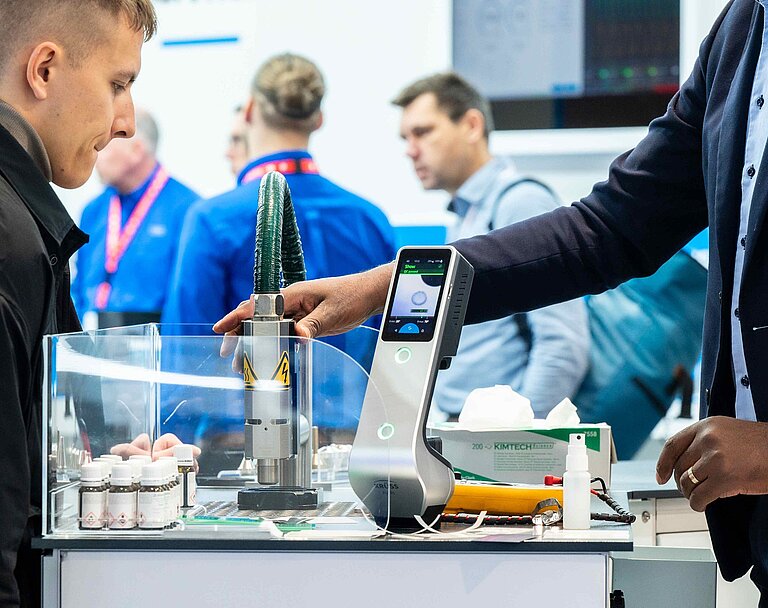
At booth 169 in Hall 7, we’ll demonstrate live how oxide layers can be removed automatically and inline, and how our PlasmaPlus® coating technology effectively prevents delamination during overmolding. Visit us on-site and discover what future-ready surface treatment looks like – precise, cleanroom-compatible, and environmentally friendly.
Challenges in Semiconductor and Power Module Production

Tough Demands on Materials and Interconnections
High-performance power modules must operate reliably for years under extreme conditions. Whether in electric vehicles, wind turbines, or industrial drives, these components are exposed to high temperatures, high voltages, and intense mechanical stress – all within increasingly compact designs.
A particular challenge lies at so-called “triple points,” where different materials such as copper, ceramics, and potting compounds meet. These zones are prone to stress, trapped air, or adhesion failure – all of which can shorten the module’s lifespan. One of the root causes: oxidized metal surfaces that compromise solderability and increase contact resistance. Epoxy delamination during overmolding is another common risk. To address these issues, reliable interconnect technology and targeted surface treatment are essential.
Live Demo at PCIM Europe
Experience our plasma technology live at booth 169 in Hall 7. In a fully automated demo cell, we’ll showcase both REDOX-based inline oxide reduction and functional nanocoating with PlasmaPlus® – all under realistic production conditions.
A highlight of our exhibit is the robot-controlled Plasma Treatment Unit (PTU), which allows for accurate, non-contact treatment of even complex geometries. At our interactive plasma demonstration table, you can see and feel the effects of plasma treatment for yourself – from surface cleaning and activation to improved wettability.
Our on-site experts are available to advise you on how our technologies can be tailored to your specific applications and processes.

Use Cases – Where Plasma Makes the Difference
Application Areas Across High-Demand Industries
Our plasma systems are used wherever power modules are exposed to extreme conditions and need to perform reliably. Different industries face different challenges – but the solution remains the same: advanced surface treatment with Openair-Plasma® and PlasmaPlus®.
E-Mobility
In inverters, battery management systems, and charging units, plasma ensures stable electrical contacts and prevents delamination in highly dynamic environments with intense heat and current loads.
Renewable Energy
Photovoltaic and wind energy systems require long-term durability despite exposure to UV radiation, moisture, and temperature swings. Plasma coatings help protect critical contact areas and improve reliability.
Industrial Automation
Power modules in industrial and robotic systems must withstand vibration, dust, and harsh media. Plasma treatment improves adhesion of potting compounds and ensures long-lasting, high-integrity connections.
The Exhibition Warm-Up: Power Module PlasmaTalk Now Online
Le sfide principali includono:
Vuoti nelle giunzioni a saldare
- Impedenza termica ed elettrica: I vuoti possono ridurre la conduttività termica ed elettrica dei giunti di saldatura. Questo può portare a punti caldi, aumento della resistenza e potenziali guasti dovuti al surriscaldamento.
- Debolezza meccanica: I vuoti compromettono l'integrità meccanica delle giunzioni a saldare, rendendole più suscettibili a rotture e guasti sotto stress termico e meccanico.
Ossidazione delle superfici metalliche
- Scarsa adesione: Le superfici ossidate ostacolano il corretto legame tra i materiali, con conseguente delaminazione o scarsa resistenza meccanica dei componenti assemblati.
- Saldatura incoerente: Gli ossidi creano barriere che impediscono alla saldatura di bagnarsi e diffondersi uniformemente, causando giunti di saldatura deboli e inaffidabili.
Compatibilità dei materiali
- Disadattamento dell'espansione termica: Materiali diversi hanno coefficienti di espansione termica diversi. In assenza di un trattamento superficiale e di tecniche di incollaggio adeguati, i cicli termici possono provocare tensioni che portano alla delaminazione o alla fessurazione.
- Incompatibilità chimica: I materiali devono essere selezionati e trattati con cura per evitare reazioni chimiche che possono degradare le prestazioni o causare guasti.
Residuo di flusso
- Contaminazione: I residui di flusso possono contaminare il gruppo, causando cortocircuiti elettrici, corrosione e problemi di affidabilità.
- Sfide di pulizia: Man mano che i componenti diventano più piccoli e più densamente imballati, la rimozione dei residui di flussante senza danneggiare i componenti diventa sempre più difficile.
Miniaturizzazione
- Requisiti di precisione: I componenti più piccoli e i passi più fini richiedono processi di produzione estremamente precisi. Anche piccole imperfezioni possono causare problemi di prestazioni o guasti significativi.
- Dissipazione del calore: Una dissipazione efficiente del calore diventa più impegnativa con la diminuzione delle dimensioni dei componenti, e richiede giunti di saldatura e materiali di alta qualità per gestire efficacemente il calore.
Affidabilità a lungo termine
- Esposizione ambientale: L'elettronica di potenza è spesso esposta ad ambienti difficili, tra cui temperature elevate, umidità e vibrazioni. Assicurarsi che tutti i materiali e le giunzioni siano privi di vuoti e difetti è fondamentale per mantenere l'affidabilità a lungo termine.
- Invecchiamento e degrado: Con il tempo, i materiali possono degradarsi e le giunzioni indebolirsi. I vuoti e le imperfezioni accelerano questo processo, portando a guasti precoci.

Affrontare queste sfide
Tecniche come la tecnologia Openair-Plasma® e la riduzione dell'ossido in linea di REDOX-Tool possono pulire e preparare efficacemente le superfici, assicurando che tutti i materiali si leghino correttamente e funzionino in modo affidabile anche in presenza di elevate esigenze dell'elettronica di potenza.
Ciò si traduce in migliori prestazioni elettriche, tassi di rendimento più elevati e una maggiore affidabilità e longevità complessiva dei componenti.